 Modern medicine is an amazing application of science and technology to improve the health of patients. Doctors, nurses and other healthcare workers utilize some of the most advanced equipment available to diagnose and treat diseases. New medications are formulated or discovered frequently; thanks to innovative developments. Further, geneticists are deciphering the DNA code and discovering which genes are responsible for a variety of inheritable conditions. Artificial intelligence is being applied to help solve perplexing health problems that, until now, were thought to be beyond reach.
Modern medicine is an amazing application of science and technology to improve the health of patients. Doctors, nurses and other healthcare workers utilize some of the most advanced equipment available to diagnose and treat diseases. New medications are formulated or discovered frequently; thanks to innovative developments. Further, geneticists are deciphering the DNA code and discovering which genes are responsible for a variety of inheritable conditions. Artificial intelligence is being applied to help solve perplexing health problems that, until now, were thought to be beyond reach.
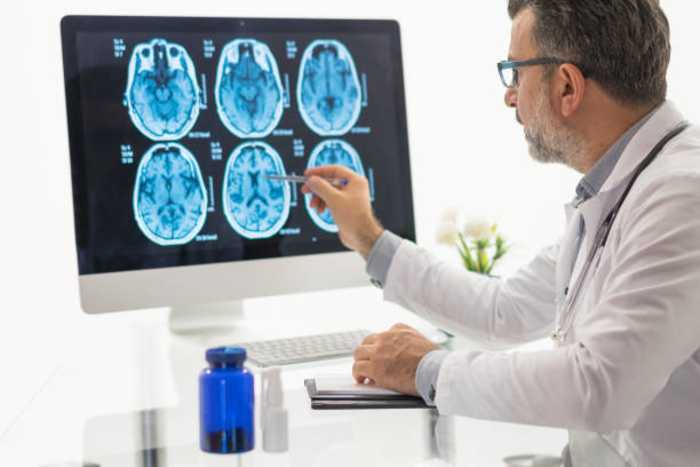
One area of health sciences where progress has been rapid is imaging. X-rays literally peek inside the human body without using a scalpel. The various types of medical imaging today have sprung from that beginning and today include an array of different imaging techniques and equipment. Three types of medical imaging utilized today are fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). Each of these uses different mechanisms and techniques. For instance, fluoroscopy equipment captures moving x-ray images like video clips.
Fluoroscopy
This form of imaging uses continuous x-ray images that allow the recording of the movement of instruments, medical implants, contrast dyes and specific anatomical areas. As with any medical procedure, this process includes some risk from exposure to radiation.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
The MRI employs very strong magnetic fields and the effect they have on molecules inside the body to record images. One advantage of this test is that it lacks the risk from exposure to radiation. MRI results are stored in slices that allow technicians to create a three-dimensional image.
Computed Tomography (CT)
CT procedures give physicians yet another view of internal processes in the body. It is another radiological test that captures still images rather than moving images like the fluoroscopy. Also, similar to the MRI exam, images resulting from the CT are stored in slices that allow the reconstruction of three-dimensional images.
Imaging procedures improve patient care and treatment by helping doctors treat their patients more effectively. These and other imaging techniques in the arsenal of medical diagnostic tools empower physicians with pictures that truly are worth a thousand words.
